Nursing Home Statistics in 2025
According to the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) data, the United States contains 15,600 nursing homes with over 1.7 million total licensed beds. While the overall occupancy rates of these facilities decreased during the pandemic, a decrease that has held strong over the past couple of years, nursing homes still represent a vital source of housing and care for a large number of seniors.
What Is a Nursing Home?
A nursing home is a type of residential care facility that provides 24/7 care, both medical and nonmedical. Generally, residents of nursing homes are medically stable but can’t return home due to mobility issues and/or the need for chronic condition care.
Unlike assisted living, which focuses almost exclusively on assistance with activities of daily living (ADLs), nursing homes will also provide chronic condition care, rehabilitative therapies, and palliative care, among other things.
Nursing Homes vs. Skilled Nursing Facilities
While the terms are often used interchangeably, nursing homes generally refer to facilities that offer permanent or long-term care, while skilled nursing facilities offer temporary care for residents while they undergo necessary rehabilitative treatment.
That said, stays in nursing homes can be temporary, and stays in skilled nursing facilities can last many days. That’s why Medicare will cover skilled nursing facility stays for up to 100 days.
Nursing Home Statistics
The Nursing Home Industry
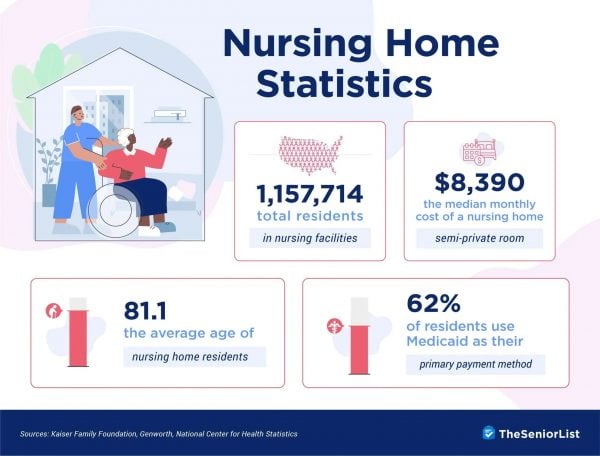
- Nursing homes served 1.16 million seniors in 2022, down from 1.37 million in 2015 but up from the pandemic low of 1.1 million in 2021.
- Nursing homes have a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.4 percent through 2030, with a current market value of $179 billion as of 2022.
- The most prominent nursing home companies include Genesis Healthcare, Lincare, The Ensign Group, and Brookdale Senior Living Solutions.
- According to the CDC, 70 percent of nursing homes are for-profit organizations, 23.2 percent are nonprofits, and 6.8 percent are government institutions.
- Nursing home residents account for less than 0.5 percent of the U.S. population, but they accounted for over 21 percent of reported COVID-19-related deaths.
Nursing Home Costs
- 62 percent of nursing home residents use Medicaid as their primary payment method, followed by Medicare (13 percent) and various other methods like private insurers and upfront payments (25 percent).
- In 2023, nursing homes cost an average of $8,390 per month for a semiprivate room and $9,584 per month for a private room.
- The most expensive state for nursing home care is Alaska, with costs averaging $33,431 per month, followed by Connecticut, with costs averaging $16,094/month.
- Long-term care coverage accounts for 32 percent of total Medicaid spending.
- The average total cost of long-term care services for seniors is $138,000.
Nursing Home Residents
- While the average length of long-term care is one year, 33 percent of today’s seniors are projected to require over two years of care.
- According to the CDC, 36.4 percent of nursing home residents are over the age of 85, 27.2 percent are between the ages of 75 and 84, 19.5 percent are 65-74, and 16.9 percent are under the age of 65.
- 63.3 percent of nursing home residents are female, while 36.7 percent are male.
- 73.9 percent of residents are non-Hispanic White in ethnicity, 14.9 percent are non-Hispanic Black, 5.7 percent are Hispanic, and 5.5 percent are other.
- 96.5 percent of residents need help with at least one ADL, with bathing being the most prominent, followed by dressing (92.7 percent) and walking (92.4 percent).
- 48.8 percent of nursing home residents experience depression, 76.9 percent experience high blood pressure, and 34.8 percent have diabetes.
Nursing Home Services
- 49.1 percent of nursing home residents require services related to Alzheimer’s or other forms of dementia.
- 63.6 percent of nursing homes offer mental health and counseling services, while 71.5 percent offer dietary and nutritional supervision.
- About 70 percent of nursing homes offer on-site pharmacy services.
- According to the CDC, 13.4 percent of nursing homes have a wing, floor, or unit designated for residents with dementia.
Nursing Home Abuse
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 66 percent of nursing home staff admitted to committing some form of elder abuse within the last year.
- Around 15.7 percent of seniors reported institutional abuse in a long-term care facility in the last year.
- For these seniors, 11.6 percent of the abuse was psychological in nature, 6.8 percent was financial, 4.2 percent was neglect, 2.6 percent was physical, and 0.9 percent was sexual.
- When also accounting for the reports of institutional abuse by the seniors’ families and proxies, the prevalence of this abuse increased anywhere from 1 to 22 percent.
- Some studies show that as few as 4 percent of elder abuse cases are reported.
Nursing Home Staff
- According to the CDC, 62.8 percent of nursing home staff members are certified social workers, 22.3 percent are licensed practical nurses, and 12.1 percent are registered nurses.
- 82 percent of long-term care workers are women, 38 percent are over the age of 50, and 26 percent are black.
- 84 percent of nursing homes report seniors staffing shortages while 96 percent report difficulties in hiring additional staff.
- 54 percent of nursing homes turn away prospective residents due to staffing shortages
- Turnover rates for nursing homes are so high that data from the American Health Care Association and National Center for Assisted Living (AHCA/NCAL) predicts that they won’t return to pre-pandemic employment levels until 2027.
Bottom Line
Despite the slight decrease in total residents, nursing facilities still provide an essential source of housing and care for seniors. Costs for nursing homes also continue to rise, making it essential for families to plan for this type of care.
To learn more about nursing homes, how they work, and how to pay for them, read our helpful guides: